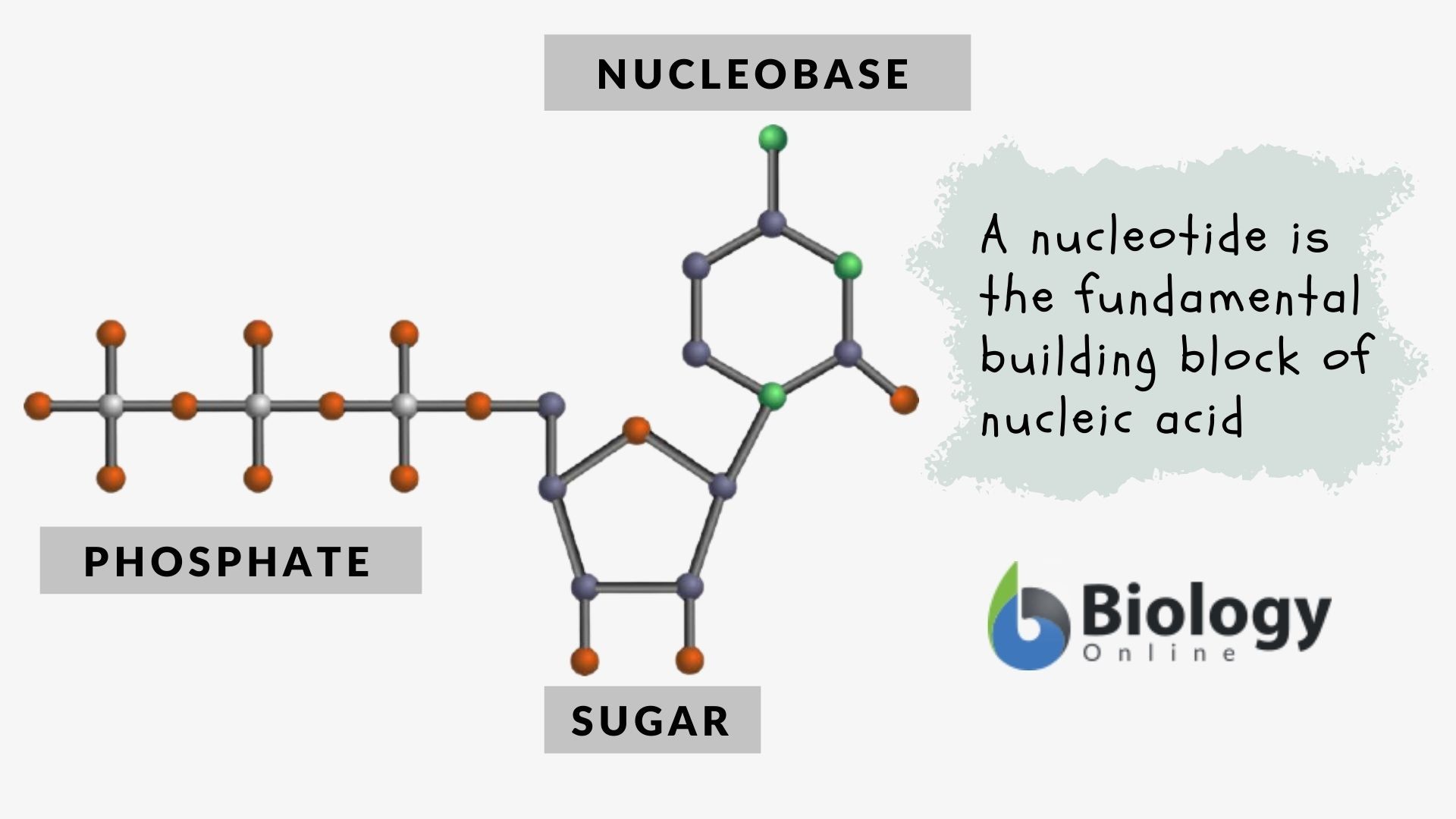
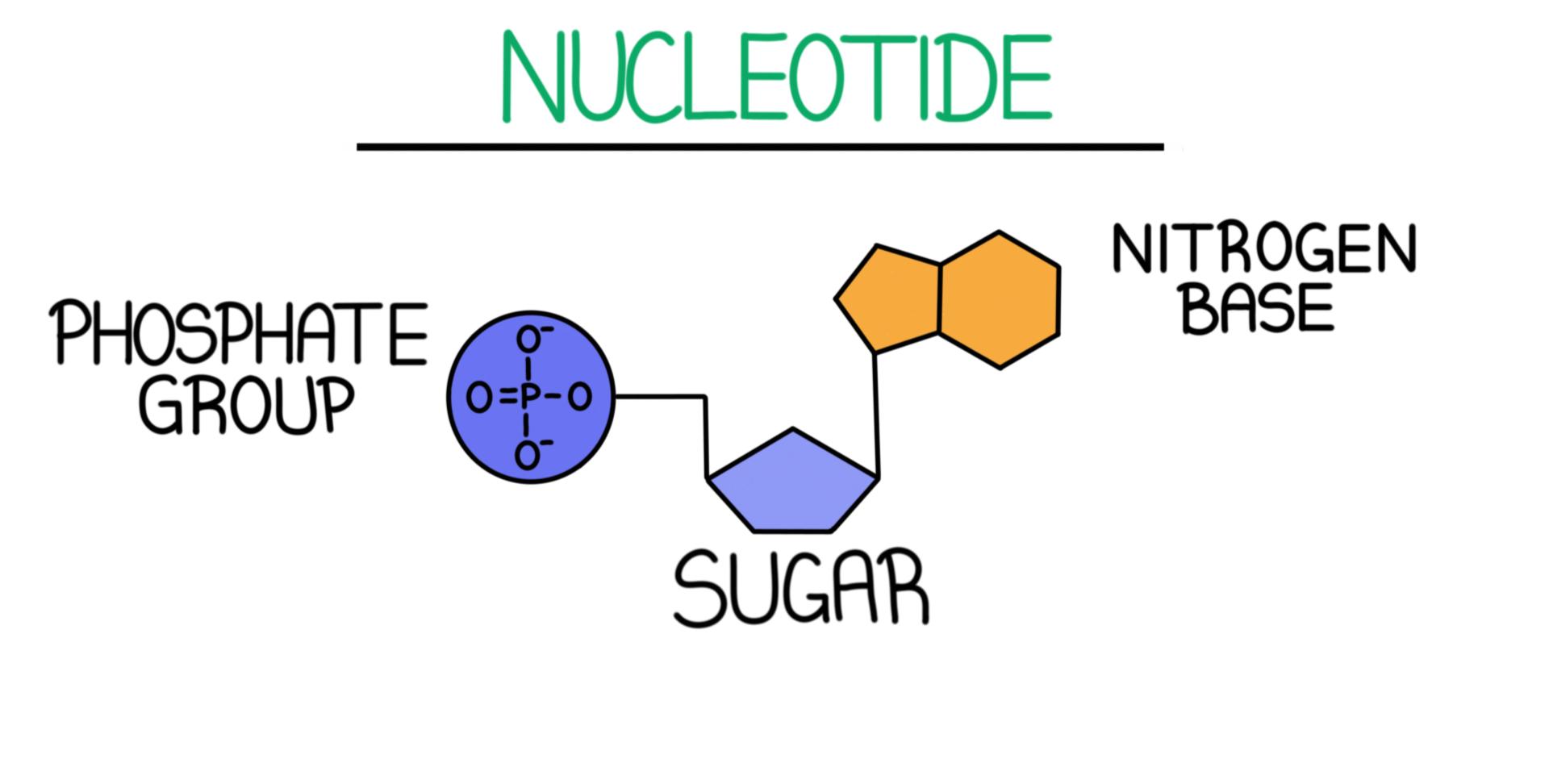
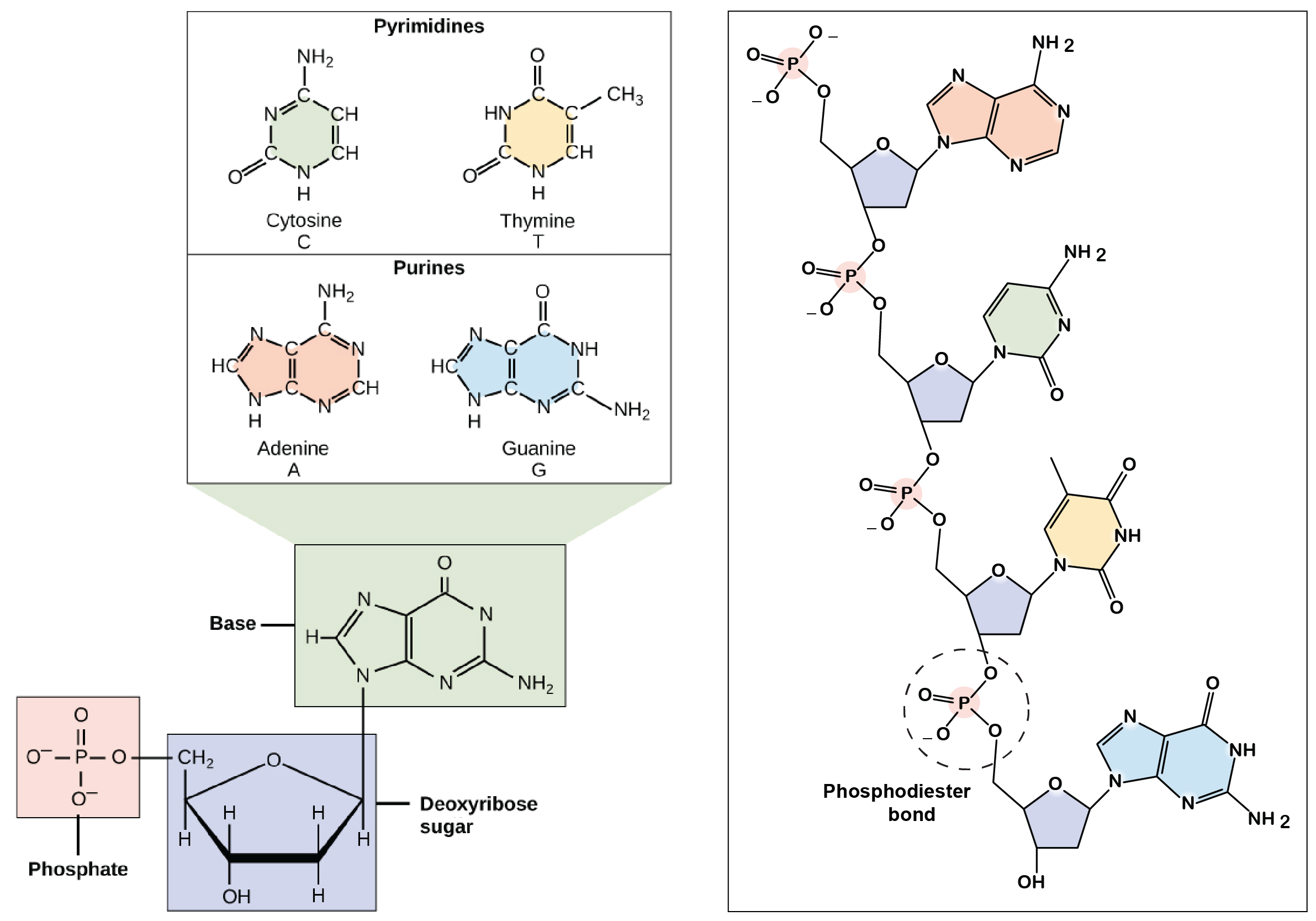
Drawing Of Nucleotide
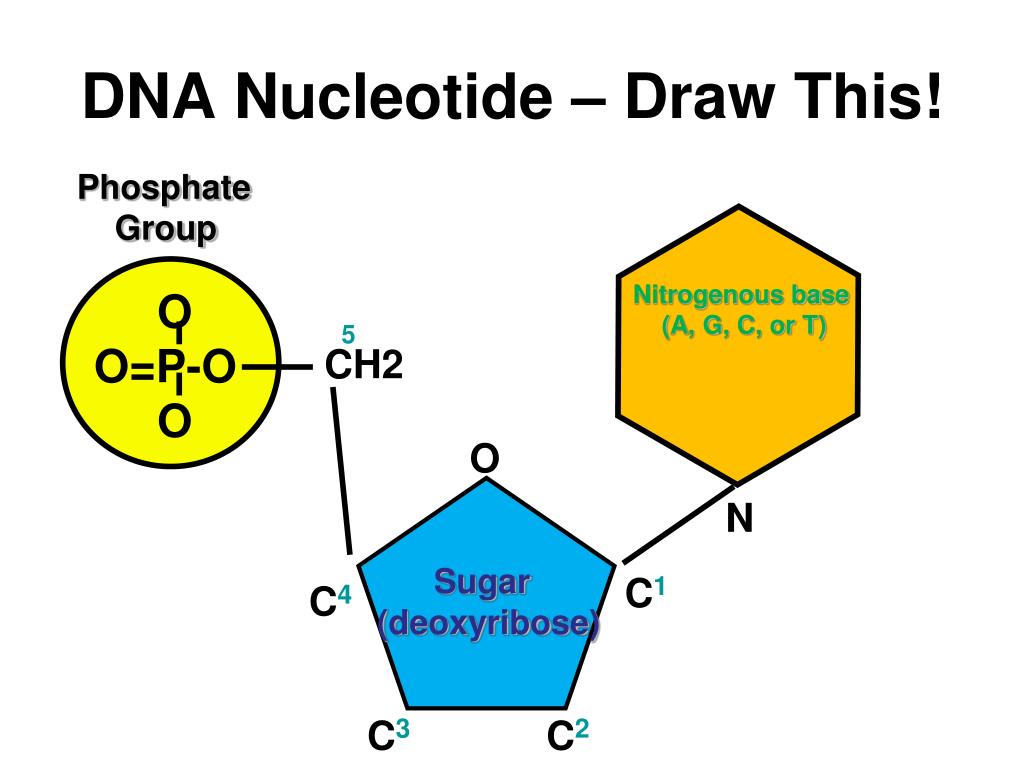
Drawing Of Nucleotide - In order to discuss this important group of molecules, it. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The bases used in dna are adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g) and thymine (t). There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. Web both deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web the term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). The two types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). In rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Web both deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: Here, we'll take a look at four major types of rna: They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. An organic compound made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. An organic compound made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: Web both deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Dna and rna are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. The bases used in dna are adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g) and thymine (t). Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides,. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. Web nucleic acids are molecules that store and replicate information for cellular growth and reproduction. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. A nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in. The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. There are four nitrogenous bases in dna, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. There are four nitrogenous bases in dna, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show how the nucleotide units are joined together. An organic compound made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. This instructional video outlines the external and internal. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′ (the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base, which are numbered without using a prime notation). A nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. Adenine and guanine are purines. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Web nucleic acids are molecules that store and replicate information for cellular growth and reproduction. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. The bases used in dna are adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g) and thymine (t). Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine or pyrimidine base attaches to the sugar component in nucleotides and nucleosides.Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Nucleotide
PPT DNA History, Structure and Replication PowerPoint Presentation
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Structure Of DNA Function, Summary, Diagram & Model
Draw And Label The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Pensandpieces
Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning · Anatomy and Physiology
Nucleotide Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Nucleotides DNA Diagram Labeled Simple
What Is The Basic Shape And Makeup Of A Nucleotide Mugeek Vidalondon
There Are Four Nitrogenous Bases In Dna, Two Purines (Adenine And Guanine) And Two Pyrimidines (Cytosine And Thymine).
Web Draw The General Structure Of A Nucleotide And A Nucleoside.
The Sugar In All Four Nucleotides Is Called Deoxyribose.
Nucleic Acids, Crucial Macromolecules For Life, Were First Discovered In Cell Nuclei And Exhibit Acidic Properties.
Related Post:
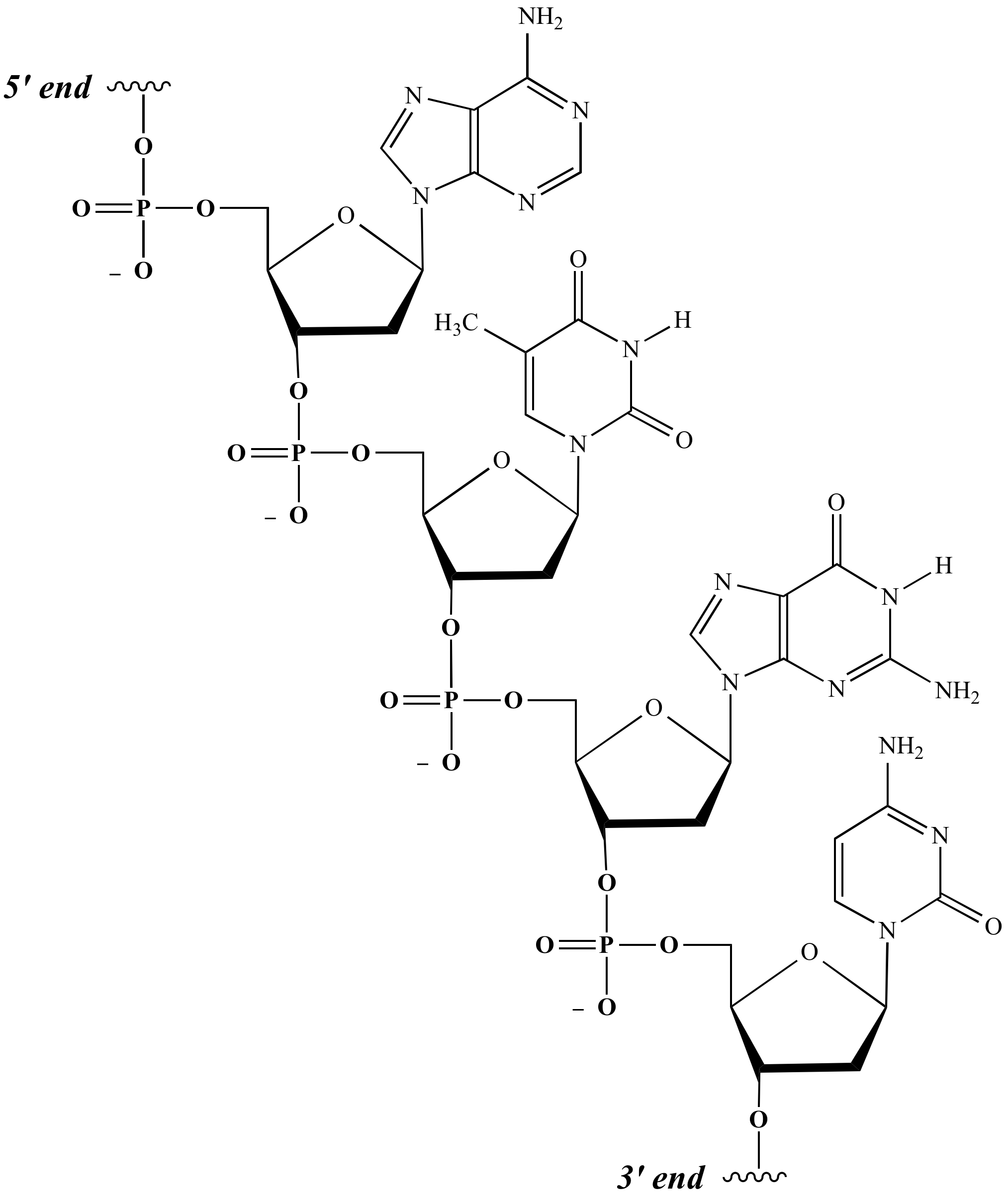


/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)